 13 min
13 min 4.5K
4.5KBlockchain Breakdown: What is a Layer 2?
Unscrambling Layer 2 Solutions: How They Boost Blockchain Scalability and Speed

Intro
Crypto’s getting bigger by the day. As of June 2024, there were 617 million crypto owners and the total market cap was $2.24 trillion. But even with this massive growth, blockchain technology still has a major issue: scalability. Ethereum’s mainnet has a throughput of around 15-30 transactions per second (TPS), which isn’t fixed. It can vary slightly based on block size and network activity. Also, Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) with Ethereum 2.0 will improve scalability, especially when combined with sharding.
Think of Layer 2 (L2) solutions as the turbo boost for blockchain. They’re off-chain technologies built on top of the main blockchain, Layer 1 (L1) to make transactions faster, cheaper and more efficient. Some L2s like Arbitrum, Polygon, Optimism etc. can handle 4,000 transactions per second. Not that they do it daily, but they can when needed, which is a huge upgrade from the usual speed. This throughput means we can have more complex apps like DeFi, gaming and supply chain stuff running smoothly on blockchain.
In a word, while Layer 1 is busy with big changes like increasing block sizes, Layer 2 uses clever tricks like rollups and sidechains to speed things up without sacrificing security. In this article we’ll dive deep into Layer 2 and see how it’s going to change the world of blockchain.
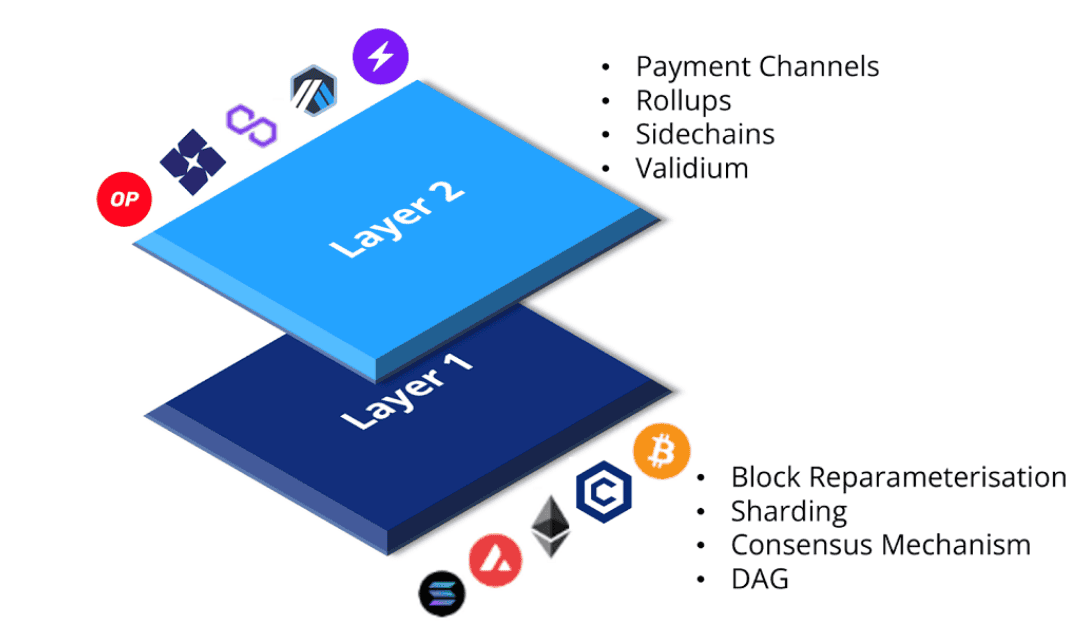
A visual comparison of Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchain solutions, showing their key technologies and examples
Layer 2 scaling solutions offload the computation and storage burden from Layer 1 while maintaining security through periodic commitments or fraud proofs.
Think of it as speeding up your internet connection but for blockchain.
There are a few ways to build Layer 2 like rollups, state channels and sidechains. It’s like choosing the right tool for the job. Some are better for certain tasks but they all make blockchain faster and more efficient.
Blockchain is getting bigger and bigger and Layer 2 is going to be essential for keeping it running smoothly.
What is a Layer 2 Solution?
Layer 2 solutions are like the secret sauce that takes blockchain tech to the next level, tackling the major headaches that traditional Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum can’t always handle. Sure, Layer 1 blockchains do the heavy lifting—they process transactions and keep things secure with consensus methods like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). But they often run into trouble when it comes to scaling. This issue is part of the "blockchain trilemma," which says it’s tough to nail down scalability, security, and decentralization all at the same time. Because of this, Layer 1 networks can slow down, leading to longer wait times and higher fees, especially when things get busy. Layer 2 solutions step in to keep everything running smoothly, even when the network’s under pressure.
For example, the Lightning Network is one of several Layer 2 solutions for Bitcoin, not the only one, making transactions faster and cheaper by taking them off the main blockchain for a bit. Imagine you and a friend open up a private payment channel, which is like a digital ledger just between the two of you. And yet, while the transactions happen off-chain in the Lightning Network, they are still backed by Bitcoin’s Layer 1 security model through hash timelock contracts (HTLCs), which ensure that funds are safely settled on the main chain in the event of a dispute The cool part is that you only need to update the blockchain twice: once when you open the channel and once when you close it. This way, the blockchain doesn’t get bogged down with every single transaction, making the whole process quicker and cheaper. Ethereum’s rollups—Optimistic Rollups and Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Rollups—work a bit differently but with the same goal of reducing the load on the main blockchain. So, which scaling solutions do exist out there?
Ethereum’s Layer 2 Scaling
Rollups
Rollups are software protocols that work on top of the mainchain, streamlining transactions and reducing congestion. Optimistic Rollups, such as Base, Arbitrum, Optimism, Boba Network, bundle multiple transactions into a batch and submit this compressed batch as call data to the Ethereum main chain. Here’s where it gets interesting: these rollups assume that transactions are valid and submit transaction data to the main chain without performing the computation on-chain. If a dispute arises, transactions can be verified through a challenge mechanism that ensures their validity. However, if someone suspects there’s a mistake or a fraudulent transaction, they can initiate a fraud proof during the challenge window. If the proof is successful, the batch is rolled back, and the submitter may lose a deposit. Fraud proofs in Optimistic Rollups work by disputing potentially invalid state transitions, which then trigger on-chain verification This system reduces the amount of computation the main chain has to do, making things faster and cheaper, but it’s still secure because of this challenge mechanism.

ZK Rollup Structure
ZK Rollups, on the other hand, take a different approach. Instead of assuming everything is fine until proven otherwise, ZK Rollups use cryptographic proofs, specifically zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge (zk-SNARKs) or zk-STARKs to validate a batch of transactions off-chain They generate what's called a 'succinct proof' (often a SNARK or STARK) for each batch of transactions." This proof is a super-efficient way to prove that all the transactions in the batch are valid without having to go through each one individually on the Ethereum main chain. The main chain just verifies this proof, which is really quick, and then it can confidently accept the whole batch of transactions. This method is super secure and efficient, though it’s a bit more complex technically.
Side Chains
Another kind of a scaling solution. side chains are almost like parallel universes, operating as separate blockchains alongside the mainchain.Binance Smart Chain (now known as BNB Smart Chain) and Avalanche are Layer 1 blockchains with their own consensus models, not strictly Layer 2 sidechains to Ethereum. Polygon operates as both a Proof of Stake sidechain and an aggregator of Layer 2 solutions have got their own set of validators and consensus mechanisms, which means they can handle transactions on their own, without relying on the main chain for everything. The cool part is that sidechains typically rely on bridges (e.g., Plasma bridges or smart contracts) to facilitate asset transfers, which may not always function as a true two-way peg like in Bitcoin's Liquid network. This lets you transfer assets between the main chain and the sidechain, which is especially popular for users looking to take advantage of different networks’ unique features or lower transaction fees. Sidechains often use bridges to make this happen, allowing for smooth communication and asset transfers between the two chains, even though their consensus mechanisms might be totally different.

Side Chain Structure
State Channels
Yet another scaling product is state channels. State channels are off-chain mechanisms that allow users to perform multiple transactions privately without broadcasting each transaction to the blockchain. Only the opening and closing transactions are recorded on-chain, reducing congestion and speeding up interactions. State channels are off-chain mechanisms that allow participants to transact directly with each other without needing to record every interaction on the main chain. Only the final state is settled on-chain.

Lightning network implemented on top of Bitcoin
Imagine how you and your friends can talk privately. Instead of shouting out every message to the whole world, you just keep track of your conversation and only tell everyone the final result. This is how state channels work. State channels require the initial channel setup and final settlement to occur on-chain, using a multi-signature wallet to ensure that the off-chain transactions are mutually agreed upon by participants. Also, note that state channels are primarily useful for repeated, small-value transactions (micropayments) and not for complex smart contract interactions. This is super efficient for things like gaming or tiny payments
Plasma
Plasma is totally different in a way that it is a framework that hosts a family of smaller blockchains connected to the main blockchain. These smaller blockchains, often called child chains, operate under their own rules and validators but rely on periodic commitments to the mainchain for security. While Plasma provides scaling benefits, it faces challenges such as slow finality and potential data availability issues. Plasma has seen reduced adoption due to its limitations in security and finality, as users must wait through lengthy exit periods (often 7-14 days) to withdraw funds back to Ethereum. It’s essential to point out that Plasma has been somewhat overtaken by rollups, which are more efficient and secure, and one of the earliest and most well-known implementations of Plasma is OMG Network.

Plasma Chain Structure
Periodically submitting the final transaction states back to Ethereum for validation, ensuring security and finality, Plasma chains handle a high volume of transactions off-chain, but they are limited in supporting complex smart contracts and have seen reduced adoption due to their slow withdrawal times. Their primary use cases were initially aimed at applications requiring simple transfers, though newer solutions have overtaken Plasma.
By reducing the load on Ethereum’s mainnet, Plasma lowers fees and speeds up transactions. However, withdrawing funds from Plasma chains to Ethereum can take up to 7 days, as this period is necessary to allow for any potential disputes or fraud detection before the funds are fully available on the main chain."
Examples of Layer 2 Solutions
Several Layer 2 solutions have been successfully implemented across various blockchain networks. Here are some notable examples:
1. Optimism
- Type: Optimistic Rollup
- Description: Optimism is an Ethereum Layer 2 solution that utilizes Optimistic Rollups to increase transaction throughput. It assumes transactions are valid and only performs a computational check if a challenge is raised. Optimism reduces the computation required on-chain through the use of fraud proofs, while still submitting minimal transaction data (compressed) to Layer 1, significantly lowering gas fees and increasing transaction speed.
- Use Cases: DApps, DeFi protocols, and any Ethereum-based projects needing scalability.
2. Arbitrum
- Type: Optimistic Rollup
- Description: Arbitrum is another Layer 2 solution based on Optimistic Rollup technology. It enhances Ethereum’s scalability by moving most of the transaction processing off-chain while maintaining the security of Ethereum's mainnet. Arbitrum is known for its compatibility with existing Ethereum smart contracts, making it easy for developers to migrate their applications.
- Use Cases: DeFi, gaming, and other high-transaction applications.
3. Polygon (formerly Matic)
- Description: Polygon is a multi-chain Layer 2 solution that provides a framework for building interconnected blockchain networks. It combines Proof-of-Stake (PoS) side chains and Plasma technology to offer a scalable solution with fast transaction processing and low fees. Polygon's PoS chain runs parallel to Ethereum and supports a wide range of decentralized applications.
- Use Cases: NFTs, DeFi, gaming, and various DApps.
4. zkSync
- Type: Zero-Knowledge Rollup (zk-Rollup)
- Description: zkSync is a Layer 2 solution utilizing Zero-Knowledge Rollups, which use cryptographic proofs to validate transactions. This allows for highly efficient and secure transaction processing off-chain, with the validity of these transactions proven on-chain through succinct cryptographic proofs. zk-Rollups inherit the full security of Layer 1, unlike Optimistic Rollups which rely on the challenge mechanism for security
- Use Cases: Payment systems, DeFi applications, and token transfers.
5. Loopring
- Type: Zero-Knowledge Rollup (zk-Rollup)
- Description: Loopring is a decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol that leverages Zero-Knowledge Rollups to facilitate high-throughput, low-cost trading on Ethereum. By bundling transactions off-chain and verifying them with zk-proofs, Loopring allows users to trade assets with minimal fees and fast execution.
- Use Cases: Decentralized exchanges, payment solutions, and DeFi.
6. Immutable X
- Type: Zero-Knowledge Rollup (zk-Rollup)
- Description: Immutable X is a Layer 2 solution specifically designed for NFTs on Ethereum. It uses zk-Rollups to enable fast and gas-free minting, buying, and selling of NFTs. Immutable X striving for carbon neutrality through Layer 2 scaling, reducing energy consumption compared to Ethereum’s Layer 1 transactions, making it an eco-friendly option for NFT platforms.
- Use Cases: NFT marketplaces, gaming platforms, and digital art.
7. StarkNet
- Type: Zero-Knowledge Rollup (zk-Rollup)
- Description: StarkNet is a decentralized zk-Rollup that allows any decentralized application (DApp) to achieve unlimited scalability without compromising Ethereum’s composability and security. It uses STARKs (Scalable Transparent ARguments of Knowledge) to ensure the validity of off-chain transactions, making it highly secure and scalable.
- Use Cases: Complex DApps, DeFi, gaming, and more.
Layer 2 Benefits
Layer 2 products help blockchains solve some of their biggest problems, especially scaling, cost, speed and privacy. By handling transactions off the main chain, Layer 1, they make blockchain networks way more capable, so they can serve more users and process more transactions without compromising security or decentralization. This means lower transaction costs, making blockchain more accessible to everyone, and faster, which is crucial for real-time applications like gaming and finance. And some L2s even offer better privacy by keeping more transaction details off the public chain.
Scalability
Like a traffic cop, L2s clear the congestion and let networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin handle way more transactions. Without them it’s like trying to drive on a highway during rush hour—slow and frustrating! Layer 2 solutions expand blockchain capacity, enabling higher throughput and lower latency, which is critical for high transaction volume applications.
Lower Costs
Layer 2 protocols also make transactions way cheaper by taking some of the load off the main network. This is big for busy areas like DeFi and gaming where high fees are a major pain.
Faster Transactions
Speed is key in blockchain and L2s deliver near-instant transaction confirmations. By handling transactions off-chain and only recording the final state on the main chain, Layer 2 networks avoid the delays that come with Layer 1 block confirmations
More Privacy
Privacy is getting more important every day and some L2s like Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Rollups offer more privacy features. By processing transactions off-chain, these solutions keep most transaction details off the public blockchain, hiding user identities and sensitive info.
Layer 2 in the Future
As blockchain grows the need for scalable, efficient and user-friendly products will only increase. Future developments will focus on seamless integration with Layer 1 blockchains, expanding use cases across industries and interoperability between different L2 networks. These will help blockchain scale globally without sacrificing security or decentralization, making Layer 2 a key player in the future of blockchain. Check it out.
Layer 1 Integration
One big goal for L2s is to make them work with Layer 1 blockchains. As these technologies evolve the connection between the main chain and its L2 extensions will need to become more seamless and user-friendly. Imagine switching between different layers without any hassle—this means your experience will be much smoother and you won’t have to deal with complicated processes. We might see new tools and features that automatically shift transactions to L2 when L1 gets crowded or that make it easier to use these technologies without having to understand all the details. This will make blockchain networks more stable and secure and able to handle more traffic without slowing down.
Expanding Use Cases
L2s are pretty versatile and their use goes far beyond just scaling and cost savings in DeFi and gaming. In the future we might see them used in many different industries. For example in supply chain management they could help track goods across borders efficiently, handling lots of data with ease. Even non-blockchain industries like healthcare and telecom might start using L2 solutions to manage sensitive information. The speed, cost savings and scalability of L2 makes it a great fit for any industry that needs high performance decentralized data management. As the tech advances we’ll see L2 being used in new and innovative ways to solve industry problems.
Conclusion
L2s will be the key to the blockchain world solving the big problems of scalability, cost and usability that have held back mass adoption of decentralized networks. As these technologies advance they will make blockchain platforms work better, handle more users and transactions globally and still be secure and decentralized. The future is looking good for L2, there’s a lot to look forward to. We’ll see better integration with Layer 1 blockchains, new use cases across industries and interoperability between networks. This will not only make current blockchain systems more efficient but also open up new opportunities for decentralized apps in different industries, shaping the future of blockchain.
Layer 2 solutions are designed to enhance the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks by processing transactions off-chain, thereby reducing congestion on the main chain and lowering transaction fees.
While Layer 1 blockchains handle the core functions, including security and consensus, Layer 2 solutions operate on top of these networks to optimize performance, such as speeding up transactions and reducing costs.
Key examples of Layer 2 technologies include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum, and sidechains like Polygon, each offering different methods for scaling and enhancing blockchain operations.





















